
|
|
RESERVES: The vault cash and deposits at the Federal Reserve System that banks use to complete day-to-day transactions.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MARKET CLEARING: A condition of the market in which the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied, such that the market is "clear" of any shortage or surplus. Market clearing is a common, non-technical term for equilibrium. In a market graph, the market clearing is found at the intersection of the demand curve and the supply curve. Market clearing is achieved when the market is in balance, the quantity that buyers want to buy is equal to the quantity that sellers want to sell. Because quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal, there is no shortage nor surplus in the market, which means that neither buyers nor sellers are inclined to change the price, which is the primary condition for equilibrium.Market clearing is also characterized by equality between the demand price and supply price. This equality generates an efficient allocation of resources (presuming competition and no market failures). In common everyday use, market clearing is the common everyday term for market equilibrium. When Aunt Rita, for example, talks about the market-clearing price of gold bullion on the Swiss exchange, she is referring to the price that achieves an equilibrium balance between quantity demanded and quantity supplied. Clearing the Market| Market Clearing | 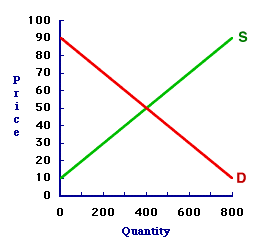 |
The market model displayed in the exhibit to the right can be used to identify the market clearing. This particular model represents the market for 8-track tapes, which are filled with the wonderful works of classic performers such as The Carpenters and Englebert Humperdink. The buyers and sellers happen to be folks attending the 88th Annual Trackmania 8-Track Tape Collectors Convention at the Shady Valley Exposition Center.Market clearing achieves a balance in the market, which is equality between quantity demanded and quantity supplied. In other words, it clears the market of any shortage or surplus. This is accomplished at the intersection of the demand curve and supply curve. This intersection point can be identified by clicking the [Market Clearing] button in the exhibit. Doing so reveals that the market is cleared at a price of 50 cents. At this price, the demand curve and supply curve intersect. The quantity demanded is 400 tapes and the quantity supplied is 400 tapes. The quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. The buyers can buy all that they want, so there is no shortage. The sellers can sell all that they want, so there is no surplus. Neither buyers nor sellers are motivated to change the price. The forces of demand and supply are in balance. This is the ONLY price that achieves a balance between these two quantities. Best of all, because this is equilibrium, the price of 50 cents will not change and the quantity of 400 tapes will not change unless or until an external force intervenes.

Recommended Citation:MARKET CLEARING, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
|
Lewis Carroll, the author of Alice in Wonderland, was the pseudonym of Charles Dodgson, an accomplished mathematician and economist.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
TI
Taxable Income
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


