
|
|
PARTNERSHIP: One of the three basic forms of business organization (the other two are corporation and proprietorship). A partnership is a business that's owned and operated more or less equally by two or more people. The owners and the business are legally considered one and the same. As such, each owner has unlimited liability, which means that an owner is held personally responsible for any and all of the business's debts, including those made by a partner.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MARGINAL REVENUE CURVE: A curve that graphically represents the relation between the marginal revenue received by a firm for selling its output and the quantity of output sold. A firm maximizes profit by producing the quantity of output found at the intersection of the marginal revenue curve and marginal cost curve. The marginal revenue curve for a firm with no market control is horizontal. The marginal revenue curve for a firm with market control is negatively sloped and lies below the average revenue curve. A marginal revenue curve is the graphical relation between the marginal revenue a firm receives from production and the quantity of output produced. The marginal revenue curve reflects the degree of market control held by a firm. For a perfectly competitive firm with no market control, the marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line. Because a perfectly competitive firm is a price taker and faces a horizontal demand curve, its marginal revenue curve is also horizontal and coincides with its average revenue (and demand) curve.For firms with more market control, especially monopoly, the average revenue curve is negatively-sloped. Because a firm with market control is a price maker and faces a negatively-sloped demand curve, its marginal revenue curve is also negatively sloped and lies below its average revenue (and demand) curve. Perfect CompetitionPerfect competition is a market structure with a large number of small firms, each selling identical goods. Perfectly competitive firms have perfect knowledge and perfect mobility into and out of the market. These conditions mean perfectly competitive firms are price takers, they have no market control and receive the going market price for all output sold.Marginal Revenue Curve,
Zucchini Style | 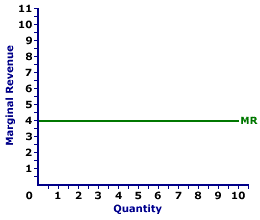 |
Marginal revenue is commonly represented by a marginal revenue curve, such as the one labeled MR and displayed in the exhibit to the right. This particular marginal revenue curve is that for zucchini sales by Phil the zucchini grower, a presumed perfectly competitive firm. The vertical axis measures marginal revenue and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of output (pounds of zucchinis). Although quantity on this particular graph stops at 10 pounds of zucchinis, the nature of perfect competition indicates it could easily go higher. This curve indicates that if Phil sells the first pound of zucchinis (an increase in production from 0 to 1), then his extra revenue is $4. However, if he sells his tenth pound (an increase in production from 9 to 10), then he also receives $4 of extra revenue. Should he sell his hundredth pound (an increase in production from 99 to 100), then he moves well beyond the graph, but his marginal revenue remains at $4. Because Phil is a perfectly competitive firm, his marginal revenue curve is also his demand curve and his average revenue curve. All three curves coincide for perfect competition. Monopoly, Oligopoly, and Monopolistic CompetitionMonopoly is a market structure with a single firm selling a unique good. As the only firm in the market, monopoly is a price maker and has extensive market control, facing a negatively-sloped demand curve. If a monopoly wants to sell a larger quantity, then it must lower the price.Marginal Revenue Curve,
Medicine Style | 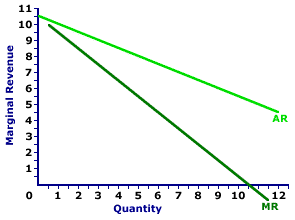 |
The marginal revenue curve (MR) for Feet-First Pharmaceutical is displayed in the exhibit to the right. Key to this curve is that Feet-First Pharmaceutical is a monopoly provider of Amblathan-Plus and thus faces a negatively-sloped demand curve. Larger quantities of output are only possible with lower prices.The vertical axis measures marginal revenue and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of output (ounces of medicine). Although quantity on this particular graph stops at 12 ounces of medicine, it could go higher. This exhibit displays both the marginal revenue curve (MR) and the average revenue curve (AR), which is also the demand curve. Both are negatively sloped, but the marginal revenue curve lies below the average revenue curve, which means that marginal revenue is less than average revenue (and price) for any given quantity. Although this marginal revenue curve is based on the production activity of Feet-First Pharmaceutical, a well-known monopoly firm, it can apply to any firm with market control. Monopolistic competition and oligopoly firms that also face negatively-sloped demand curves that generate comparable marginal revenue curves.

Recommended Citation:MARGINAL REVENUE CURVE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | |
Related Websites (Will Open in New Window)... | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BEIGE MUNDORTLE
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time strolling around a discount warehouse buying club hoping to buy either a case for your designer sunglasses or arch supports for your shoes. Be on the lookout for crowded shopping malls.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Before 1933, the U.S. dime was legal as payment only in transactions of $10 or less.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
NE
Nash Equilibrium
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


