
|
|
RELATIVELY ELASTIC: An elasticity alternative in which relatively small changes in price cause relatively large changes in quantity. In other words, quantity is very responsive to price. Relatively elastic should be compared with other elasticity alternatives--relatively inelastic, perfectly inelastic, perfectly elastic, and unit elastic.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           TOTAL REVENUE CURVE, MONOPOLY: A curve that graphically represents the relation between the total revenue received by a monopoly firm for selling its output and the quantity of output sold. It is combined with a monopoly firm's total cost curve to determine economic profit and the profit maximizing level of production. The slope of the total revenue curve is marginal revenue. Monopoly is a market structure with a single firm selling a unique good. As the only firm in the market, monopoly is a price maker and has extensive market control, facing a negatively-sloped demand curve. If a monopoly wants to sell a larger quantity, then it must lower the price.The total revenue curve reflects the degree of market control held by a firm. For a perfectly competitive firm with no market control, the total revenue curve is a straight line. For firms with more market control, especially monopoly, the total revenue curve is "hump shaped," increasing, reaching a peak, then declining. The slope of this total revenue curve is marginal revenue. Total Revenue Curve,
Medicine Style | 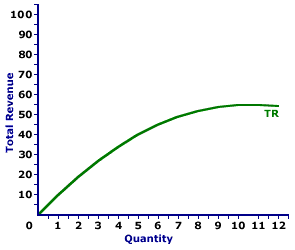 |
The total revenue curve for Feet-First Pharmaceutical is displayed in the exhibit to the right. Key to this curve is that Feet-First Pharmaceutical is a monopoly provider of a drug called Amblathan-Plus and thus faces a negatively-sloped demand curve. Larger quantities of output are only possible with lower prices.The vertical axis measures total revenue and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of output (ounces of medicine). Although quantity on this particular graph stops at 12 ounces of medicine, it could go higher. This curve indicates that if Feet-First Pharmaceutical sells 1 ounce of medicine (at $10 per ounce), then it receives $10 of total revenue. Alternatively, if it sells 10 ounces (at $5.50 per ounce), then it receives $55 of total revenue. Should it sell 12 ounces (at $4.50 per ounce), then it receives only $54 of total revenue. For Feet-First Pharmaceutical the total revenue "curve" actually is a "curve." The slope of this curve falls as more output is produced, eventually reaching a peak, then becoming negative. The changing slope of this curve is due to the changing price. Although this total revenue curve is based on the production activity of Feet-First Pharmaceutical, a well-known monopoly firm, it could also be for any firm with market control. Monopolistic competition and oligopoly firms that also face negatively-sloped demand curves generate comparable total revenue.

Recommended Citation:TOTAL REVENUE CURVE, MONOPOLY, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Related Websites (Will Open in New Window)... | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
WHITE GULLIBON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time searching the newspaper want ads seeking to buy either an extra large beach blanket or a large flower pot shaped like a Greek urn. Be on the lookout for fairy dust that tastes like salt.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
A lump of pure gold the size of a matchbox can be flattened into a sheet the size of a tennis court!
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
MMSE
Minimun Mean Square Error
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


