
|
|
VALUE IN EXCHANGE: The ability to trade an item, especially money, for other goods and services that can then be used to satisfy wants and needs. Value in exchange means that value, that is satisfaction, is obtained indirectly through the acquisition of something else. For an item to have value in exchange it need NOT have value in use, value obtained directly from the consumption of a good or service.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           AVERAGE VARIABLE COST CURVE: A curve that graphically represents the relation between average variable cost incurred by a firm in the short-run product of a good or service and the quantity produced. This curve is constructed to capture the relation between average variable cost and the level of output, holding other variables, like technology and resource prices, constant. The average variable cost curve is one of three average curves. The other two are average total cost curve and average fixed cost curve. A related curve is the marginal cost curve. The average variable cost curve is U-shaped. Average variable cost is relatively high at small quantities of output, then as production increases, it declines, reaches a minimum value, then rises. This shape of the average variable cost curve is indirectly attributable to increasing, then decreasing marginal returns (and the law of diminishing marginal returns).| Average Variable Cost Curve | 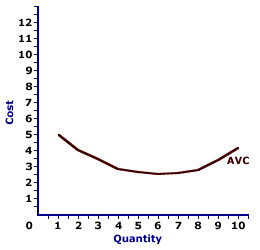 |
This graph is the average variable cost curve for the short-run production of Wacky Willy Stuffed Amigos (those cute and cuddly armadillos and tarantulas). The quantity of Stuffed Amigos production, measured on the horizontal axis, ranges from 0 to 10 and the average variable cost incurred in the production of Stuffed Amigos, measured on the vertical axis, ranges from a high of $5 to a low of $2.50, before rising again.As noted above, the average variable cost curve is U-shaped. For the first 6 Stuffed Amigos, average variable cost declines from over $5 to a low of $2.50. However, for the production of 7 (or more) Stuffed Amigos, average variable cost increases. The average variable cost curve is most important to the analysis of a firm's decision to shut down production in the short run. If price is greater than average variable cost, then a firm may or may not be receiving an economic profit, but it is better off producing in the short run than shutting down production. Shutting down production entails a loss equal to total fixed cost. However, with price greater than average variable cost, sufficient revenue is generated to pay ALL variable cost and some fixed cost, making the operating loss less than fixed cost. If price is less than average variable cost, then a firm incurs a loss greater than total fixed cost by producing. Its operating loss includes both fixed cost, plus part of the variable cost not covered by the price. As such, the firm is better off shutting down production and awaiting better times.

Recommended Citation:AVERAGE VARIABLE COST CURVE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BEIGE MUNDORTLE
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time strolling around a discount warehouse buying club hoping to buy either a case for your designer sunglasses or arch supports for your shoes. Be on the lookout for crowded shopping malls.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
North Carolina supplied all the domestic gold coined for currency by the U.S. Mint in Philadelphia until 1828.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
ADV
Ad Valorem
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


