
|
|
TEAMSTERS UNION: The common name for the International Brotherhood of Teamsters, which is one of the largest labor unions in the United States, this was established in 1903 and represents truck drivers, chauffeurs, warehouse workers, and labor in related activities. Their name was taken from the teamsters of the 1800s who guided wagons pulled by teams of horses or other animals. Their modern day counterparts have replaced teams of horses with diesel engines, but their function remains much the same. The Teamsters Union was originally part of the AFL-CIO, but was expelled in 1957 due to corruption among union leaders. The Teamsters Union rejoined the AFL-CIO in 1987.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           UTILITY MAXIMIZATION: The process or goal of obtaining the highest level of utility from the consumption of goods or services. The goal of maximizing utility is a key assumption underlying consumer behavior studied in consumer demand theory. Consumers are assumed to make choices, especially concerning the purchase of goods, such that they obtain the highest possible level of satisfaction. Utility maximization can be achieved at the peak of the total utility curve. Utility maximization is the guiding notion underlying consumer choices analyzed with consumer demand theory and utility analysis. It makes sense to think that people are generally motivated to do what is best for them, to purchase the most satisfying goods, to make the decisions that do more good than harm, to improve their overall living standards and well-being, that is, to maximize their utility.Working through the logical consequences of this assumption, when combined with other principles of consumer behavior especially the law of diminishing marginal utility, makes it possible to gain insight into such things market demand and the law of demand. The Scarcity ConnectionThe utility maximization goal is based on the seemingly obvious presumption that people prefer more to less. This presumption is tied to the unlimited wants and needs aspect of scarcity. In other words, because people have unlimited wants and needs, satisfying those wants and needs is a desirable thing to do. Someone like Duncan Thurly would rather have a full belly than an empty one. He would rather live in a cozy, climate-controlled house than in a cardboard box under a bridge.Of course, if wants and needs are unlimited, can anyone actually maximize utility? That is, can Duncan ever achieve the absolute pinnacle of satisfaction? Can he actually maximize utility. In terms of the scarcity problem, probably not. He might be able to boost utility a little higher by satisfying another unfulfilled want or need. But he is unlikely to maximize utility totally and completely. This is one reason why it is reasonable to think of utility maximization as a process of seeking what is ultimately unreachable. However, in the analysis of consumer demand theory, utility maximization has a more pragmatic interpretation--obtaining the highest possible satisfaction from consuming a given good or undertaking a specific activity. While Duncan might not be able to maximize his OVERALL utility, he can maximize the utility obtained from eating Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes. It is this pragmatic interpretation of utility maximization that pervades the study of economics. Utility Analysis| Roller Coaster Utility | 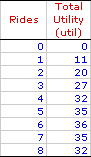 |
The accompanying table can be used to illustrate utility maximization. The numbers indicate the total utility obtained by Edgar Millbottom while riding the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster at the Shady Valley Amusement Park. The right-hand column is the accumulated satisfaction Edgar receives from riding the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster 8 times during his day at the amusement park.The numbers indicate that Edgar receives the greatest total utility, 36 utils, by riding the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster 6 times. Click the [Utility Max] button to highlight this quantity. Taking 5 trips around the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster track generates only 35 utils. Likewise, 7 rides generate only 35 utils. Maximum utility comes from 6 rides and only 6 rides. Anything else comes in less. The Peak of the Curve| Total Utility Curve | 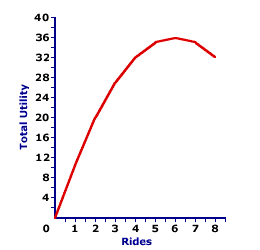 |
Utility maximization can be visually identified with a total utility curve, such as the one presented in this exhibit. In this case the maximum level of utility obtained by Edgar riding the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster is relatively obvious. The total utility curve reaches its highest point for 6 roller coaster rides. the curve increases up to the sixth ride, then declines for subsequent rides. Click the [Utility Peak] button to highlight this quantity. Real World ConstraintsIn the real world, the goal of utility maximization often encounters obstacles that prevent obtaining the highest overall level of utility. In many circumstances, consumers are unable to reach the peak of the total utility curve. Under these circumstances, consumers face a constrained utility maximization.The constraints could be physical or legal. For example, Edgar might not be able to ride the Monster Loop Death Plunge roller coaster 6 times because a bolt of lightning struck the track destroying a large section or perhaps the Shady Valley Amusement Park obtained a court order preventing Edgar for entering the park. However, the constraints facing most consumers most of the time are economic--that is, they have limited income and cannot afford to buy as much of a good as they want. If Edgar is charged $1 per ride and has only $5 of cash, then he is not able to achieve the utility maximizing 6 rides. The Essence of LifeWhile regular, everyday, noneconomist folks seldom use the term utility maximization, it is a powerful motivation force underlying a great deal (if not all) of the decisions people make and the actions they take. Again make note of the close connection between utility maximization, unlimited wants and needs, and the pervasive problem of scarcity.While Duncan might buy a freshly prepared Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae because it just "sounds tasty," what he is really trying to do is to raise his utility level to its maximum. He is motivated to eat the hot fudge sundae because it adds more to his utility total. And if he can add to his utility total, then he is not AT the maximum.

Recommended Citation:UTILITY MAXIMIZATION, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
RED AGGRESSERINE
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time at a flea market wanting to buy either a weathervane with a cow on top or a box of multi-colored, plastic paper clips. Be on the lookout for telephone calls from long-lost relatives.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
The 1909 Lincoln penny was the first U.S. coin with the likeness of a U.S. President.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
P/E
Price-Earnings Ratio
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


