
|
|
ECONOMIC POLICIES: Government actions designed to affect economic activity and pursue one or more economic goals. Also called economic policies. The four common types of government policies are: fiscal, monetary, regulatory, and judicial.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           DISEQUILIBRIUM PRICE: A price that does not achieve equilibrium in the market. A disequilibrium price is either above or below the equilibrium price. A price below the equilibrium price creates a shortage and a price above the equilibrium price creates a surplus. In both case, the market imbalance prompts the price to change, moving toward the equilibrium price. A disequilibrium price is any price that does not achieve a balance between the market forces of demand and supply. More specifically, the quantity demanded is not equal to the quantity supplied. If quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied, then a shortage exists. If quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded, then a surplus exists.Out of Balance| The 8-Track Tape Market | 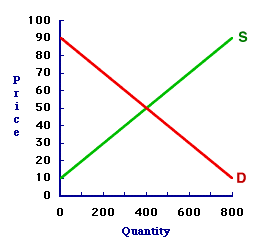 |
Disequilibrium prices that create surpluses and shortages can be illustrated using the market for 8-track tapes displayed in this exhibit. This graph was generated after long hours attending the 88th Annual Trackmania 8-Track Tape Collectors Convention at the Shady Valley Exposition Center.- 30 Cent: Consider first how a shortage is created at a 30 cent price. Click the [30 Cent] button to highlight this price. At 30 cents, the quantity demanded is 600 tapes and the quantity supplied is 200 tapes. This price does not generate equilibrium. The buyers want to buy 600 tapes, but only 200 tapes are offered for sale by the sellers. This shortage motivates buyers to offer a higher price.
- 70 Cent: Now consider how a surplus is created at a 70 cent price. Click the [70 Cent] button to highlight this price. At 70 cents, the quantity demanded is 200 tapes and the quantity supplied is 600 tapes. This price does not generate equilibrium, either. The sellers want to sell 600 tapes, but only 200 tapes are being purchased by the buyers. This surplus motivates sellers to charge a lower price.
For sake of completeness and for purposes of comparison, the equilibrium condition in the market can be identified by clicking the [Equilibrium] button. Doing so reveals an equilibrium price of 50 cents and an equilibrium quantity (without shortage or surplus) of 400 tapes.

Recommended Citation:DISEQUILIBRIUM PRICE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
|
A scripophilist is one who collects rare stock and bond certificates, usually from extinct companies.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
CAC
Consumer Advisory Council
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


