
|
|
LAW OF INCREASING OPPORTUNITY COST: The proposition that opportunity cost, the value of foregone production, increases as more of a good is produced. This "law" can be seen in the production possibilities schedule and is illustrated graphically through the slope of the production possibilities curve. It generates the distinctive convex shape of the curve, making it flat at the top and steep at the bottom.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           DEMAND PRICE: The maximum price that buyers are willing and able to pay for a given quantity of a good. While buyers might be willing and able to pay less than the demand price for a given quantity, they are not willing and able to pay more. The demand curve is a plot of the demand price for each quantity. Demand price is the highest price that buyers will pay for a good. It is based on the satisfaction buyers receive from the good in conjunction with the income buyers have available to make the purchase. While a number a factors influence the demand price, quantity demanded tends to be among the most important. The demand price is generally less if the quantity demanded is greater.Getting More For LessThis notion of demand price as a maximum comes from the fundamental economic observation that people prefer more to less. As an upper limit, demand price indicates that buyers are willing to pay less for a given quantity, but not more. By paying less for one good, buyers can use the extra to acquire more of other goods.Consider the hot fudge sundae buying preferences of Duncan Thurly. Duncan is willing and able to pay $3 for a Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundae. However, as much as he enjoys Hot Momma Fudge Bananarama Ice Cream Sundaes, he is unwilling to pay a penny more than $3. But, he would not complain if he could buy this tasty treat for $2. He would not argue if he could make the purchase for $1. In fact, he is not likely to disagree if he found it possible to buy the sundae for a zero price. The less he pays, the better. On the Demand Curve| Demand Price | 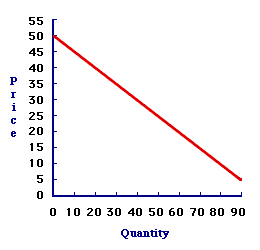 |
As the maximum price that buyers are willing and able to pay, the demand price lies ON the demand curve. In essence, the demand curve is the demand price. The demand curve plots the range of demand prices for a range of different quantities.Consider the demand curve for Quadra XE electronic calculators displayed in the exhibit to the right. For a quantity of 20 calculators, the demand price is $40. Would calculator buyers like to pay less than $40? Certainly. Would calculator buyers pay more than $40? No. The story is the same for any quantity. Only the numbers differ. For a quantity of 80 calculators, the demand price is $10. Buyers are willing to pay less than $10 for this quantity, but not more. A Lot of Demand SpaceThe area under the demand curve that includes all prices that buyers would be willing to pay is termed the demand space. It includes all prices up to and on the demand curve. Buyers are willing and able to purchase any price-quantity combination in this demand space.If buyers are able to operate beneath the demand curve, such that the price paid is less than the maximum demand price, then they obtain what is called consumer surplus. This is the extra satisfaction received by buyers over and above the price paid. And A Little CompetitionCompetition among buyers is the force that pushes the market price of a good up to the maximum demand price. This ensures efficiency, at least from the demand side of the market. With competition, buyers bid up the price until the maximum demand price is reached. If a buyer is unwilling or unable to pay that price, then they do not buy the good. Moreover, sellers have no reason to sell to any buyers offering less, because competition ensures that other buyers are willing and able to pay the demand price.

Recommended Citation:DEMAND PRICE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2025. [Accessed: July 18, 2025].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
ORANGE REBELOON
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time wandering around the downtown area trying to buy either shoe laces for your snow boots or a rim for your spare tire. Be on the lookout for the happiest person in the room.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Woodrow Wilson's portrait adorned the $100,000 bill that was removed from circulation in 1929. Woodrow Wilson was removed from circulation in 1924.
|

|
|
"A winner is someone who recognizes his God-given talents, works his tail off to develop them into skills, and uses those skills to accomplish his goals. " -- Larry Bird, basketball player
|

|
CBA
Cost Benefit Analysis
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


